How to setup a Docker Swarm cluster with Raspberry Pi's
Tue, Mar 8, 2016This week is dedicated to Docker #SwarmWeek. In this tutorial we show you how easy it is to setup a Docker Swarm with HypriotOS and the standard docker-machine binary.

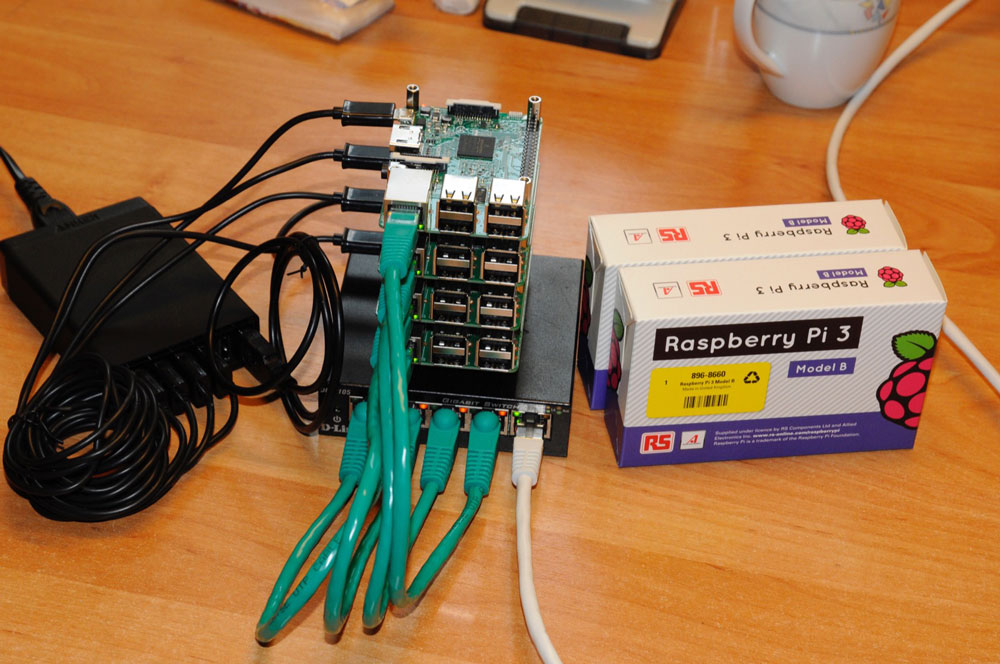
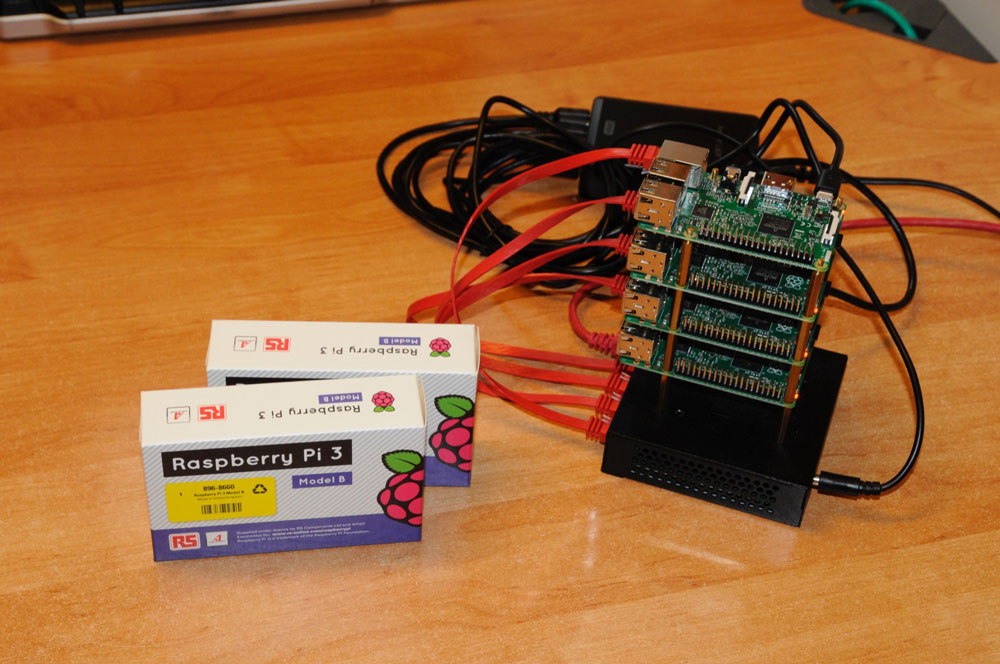
We want to setup a cluster with eight Raspberry Pi 3, grouped into two tiny datacenters with four Pi’s each.
Prepare your notebook
To control the Docker Swarm from our notebook, we have to install both docker and docker-machine binaries. If you are on a Mac, you can use brew to install them.
brew install docker
brew install docker-machine
Flash all your SD cards
Now we can easily flash the latest HypriotOS image to the eight SD cards with our flash tool and assign different node names.
flash --hostname swarm-dc1-pi01 https://downloads.hypriot.com/hypriot-rpi-20160306-192317.img.zip
flash --hostname swarm-dc1-pi02 https://downloads.hypriot.com/hypriot-rpi-20160306-192317.img.zip
...
flash --hostname swarm-dc2-pi04 https://downloads.hypriot.com/hypriot-rpi-20160306-192317.img.zip
After that, insert the SD cards and boot all the Raspberry Pi’s.
Prepare your Pi’s for docker-machine
We want to create the Docker Swarm with the standard docker-machine binary. To make this work we need to prepare the Raspberry Pi’s a little bit. The next steps are adding your SSH public key to all of your Pi’s as well as fixing the ID in /etc/os-release to debian.
function getip() { (traceroute $1 2>&1 | head -n 1 | cut -d\( -f 2 | cut -d\) -f 1) }
IP_ADDRESS=$(getip swarm-dc1-pi01.local)
ssh-keygen -R $IP_ADDRESS
ssh-copy-id -oStrictHostKeyChecking=no -oCheckHostIP=no root@$IP_ADDRESS
ssh root@$IP_ADDRESS sed -i \'s/ID=raspbian/ID=debian/g\' /etc/os-release
Repeat this for all the eight Raspberry Pi’s. You will prompted for the root password which is hypriot.
Create Swarm Token
A Docker Swarm cluster uses a unique Cluster ID to enable all swarm agents find each other. We need such a Cluster ID to build our Docker Swarm. This can be done in your shell with this command
export TOKEN=$(for i in $(seq 1 32); do echo -n $(echo "obase=16; $(($RANDOM % 16))" | bc); done; echo)
Create the swarm with docker-machine
We now create the Swarm Master on the first Raspberry Pi.
docker-machine create -d generic \
--engine-storage-driver=overlay --swarm --swarm-master \
--swarm-image hypriot/rpi-swarm:latest \
--swarm-discovery="token://$TOKEN" \
--generic-ip-address=$(getip swarm-dc1-pi01.local) \
swarm-dc1-pi01
For all the seven remaining Raspberry Pi’s we create Swarm Agents that join the Swarm cluster.
docker-machine create -d generic \
--engine-storage-driver=overlay --swarm \
--swarm-image hypriot/rpi-swarm:latest \
--swarm-discovery="token://$TOKEN" \
--generic-ip-address=$(getip swarm-dc1-pi02.local) \
swarm-dc1-pi02
After a while the whole Docker Swarm cluster with the two datacenters is up and running. We now have a cluster with 32 CPU’s and 8 GByte RAM.
Control your Swarm
To connect to your Docker Swarm use the following command to set the environment variables for the Docker Client.
eval $(docker-machine env --swarm swarm-dc1-pi01)

docker info
Containers: 10
Running: 9
Paused: 0
Stopped: 1
Images: 8
Server Version: swarm/1.1.3
Role: primary
Strategy: spread
Filters: health, port, dependency, affinity, constraint
Nodes: 8
swarm-dc1-pi01: 192.168.1.207:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 3
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:47:03Z
swarm-dc1-pi02: 192.168.1.209:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:56Z
swarm-dc1-pi03: 192.168.1.206:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:22Z
swarm-dc1-pi04: 192.168.1.208:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:51Z
swarm-dc2-pi01: 192.168.1.204:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:35Z
swarm-dc2-pi02: 192.168.1.205:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:49Z
swarm-dc2-pi03: 192.168.1.210:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:40Z
swarm-dc2-pi04: 192.168.1.211:2376
└ Status: Healthy
└ Containers: 1
└ Reserved CPUs: 0 / 4
└ Reserved Memory: 0 B / 971.8 MiB
└ Labels: executiondriver=native-0.2, kernelversion=4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+, operatingsystem=Raspbian GNU/Linux 8 (jessie), provider=generic, storagedriver=overlay
└ Error: (none)
└ UpdatedAt: 2016-03-08T17:46:37Z
Plugins:
Volume:
Network:
Kernel Version: 4.1.17-hypriotos-v7+
Operating System: linux
Architecture: arm
CPUs: 32
Total Memory: 7.592 GiB
Name: d90d49c65205

For more information about Docker Swarm you can follow the #SwarmWeek: Introduction to container orchestration with Docker Swarm.
As always use the comments below to give us feedback and share it on Twitter or Facebook.
Dieter @Quintus23M & Stefan @stefscherer
comments powered by Disqus
 Edit this blog on GitHub
Edit this blog on GitHub